Global warming
- Global warming is due to an enhanced ‘greenhouse effect’
- This enhanced effect is caused by an increase in ‘greenhouse’ gases in the atmosphere.
- Predicting the exact effects of an increase in global temperature is very difficult.
- There are many possible biological and ecological consequences of increasing temperature or Global Warming.
- It is expected that greater warming will occur at the poles more than the equator and this will effect atmospheric circulation patterns which are dependent on the temperature differences between these two areas.
- Regional rainfall patterns may also be drastically altered, which will change the patterns of world food production.
- Sea levels will rise due to -
- Melting of ice (glaciers and polar ice)
- The thermal expansion of water
- This rise will cause –
- Flooding
- Salinisation of soils
- Coastal erosion
- No one is certain how quickly it will rise but for the UK, an estimate of 0.3m to 0.6m by the year 2050.
The following table summarise these and other possible effects, some are even beneficial.
Key:-
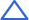 change
change
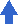 increase
increase
 leading to
leading to
 decrease
decrease
Increasing temperature |
 sea level (melting of ice and thermal expansion of water) sea level (melting of ice and thermal expansion of water)
|

|
 coastal erosion coastal erosion
|

|
 habitat loss e.g. marshes, dunes, mangroves and coral reefs. habitat loss e.g. marshes, dunes, mangroves and coral reefs.
|

|
 salinisation (more salty) of estuaries, coastal rivers and soils salinisation (more salty) of estuaries, coastal rivers and soils
|
 temperature freshwaters temperature freshwaters
|

|
 species distribution including local extinction species distribution including local extinction
|
 pattern of succession due to temperature pattern of succession due to temperature and this will favour some species more than others. and this will favour some species more than others.
|
 rainfall pattern e.g. rainfall pattern e.g. intensity and frequency (climate change) intensity and frequency (climate change) storms storms
|

|
 distribution of grasslands and savannahs and drying out of wetlands distribution of grasslands and savannahs and drying out of wetlands
|
Northern migration of boreal (evergreen/coniferous) forest |
 Forest productivity Forest productivity
|
temp was a limiting factor to growth |
 Forest productivity Forest productivity
|

|
Desiccation (drying out), causing wilting, defoliation and — fires. |
 Agricultural production Agricultural production
|

|
 yields from crops although the overall quality may be lower. yields from crops although the overall quality may be lower.
|
 water or temperature stress to animals water or temperature stress to animals
|

|
 resistance to opportunistic pests/disease e.g. coral reef organisms resistance to opportunistic pests/disease e.g. coral reef organisms
|
 in pests and disease in pests and disease
|

|
Pests and disease will move to new geographical areas e.g. spread of malaria |
 glacial melting at poles glacial melting at poles
|

|
Dramatic in food webs in food webs |

|
 productivity and biodiversity e.g. penguin populations productivity and biodiversity e.g. penguin populations
|
Solutions:
These are dealt with in detail in the Climate Change section.
 Pollution through human activities.
Pollution through human activities.

What's your opinion?
Average rating




Not yet rated